You can't. The title is worded that way to let people know there's no way to restore a crashed drive to working condition without a full wipe and/or reinstall if it was the main OS drive.
As of today, there aren't any publicly available tools or utilities that can fix filesystem errors that may happen with either internal or external drives that lose power unexpectedly.
But you can recover data from the drive using another computer/device.
There are three ways:
1. Use an iOS device with a Type-C connector, and connect the drive through a USB adapter. This can read the files directly through the Files app, allowing you to copy data right off the seemingly crashed drive. You'll need a device with enough internal storage to recover the files that you need.
2. Use a paid app, there are a few. They usually offer a free download to browse through the drive after you've connected it to another Apple computer with a USB adapter, these are about $90 for a one-month subscription but quickly give you a 50% discount if you decline to pay after the entire drive has been indexed.
3. This guide.
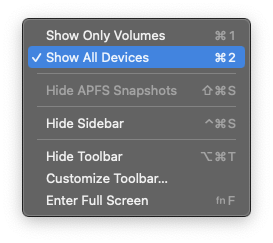
But first, the symptoms. You'll need to enable 'Show All Devices' in Disk Utility's View menu:
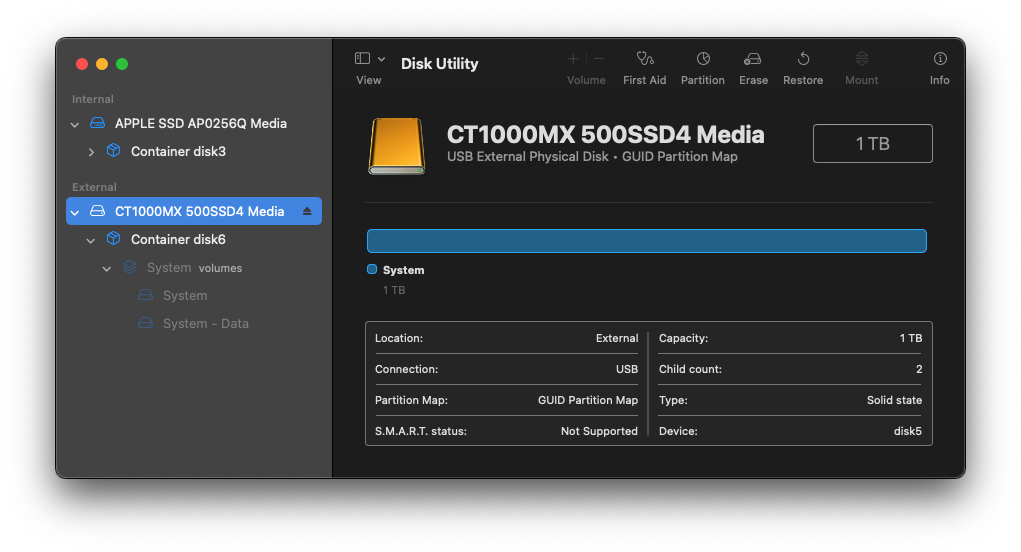
This allows you to see the APFS containers:
And when you attempt to run First Aid on the container, you get an exit code 8 with error -69716:
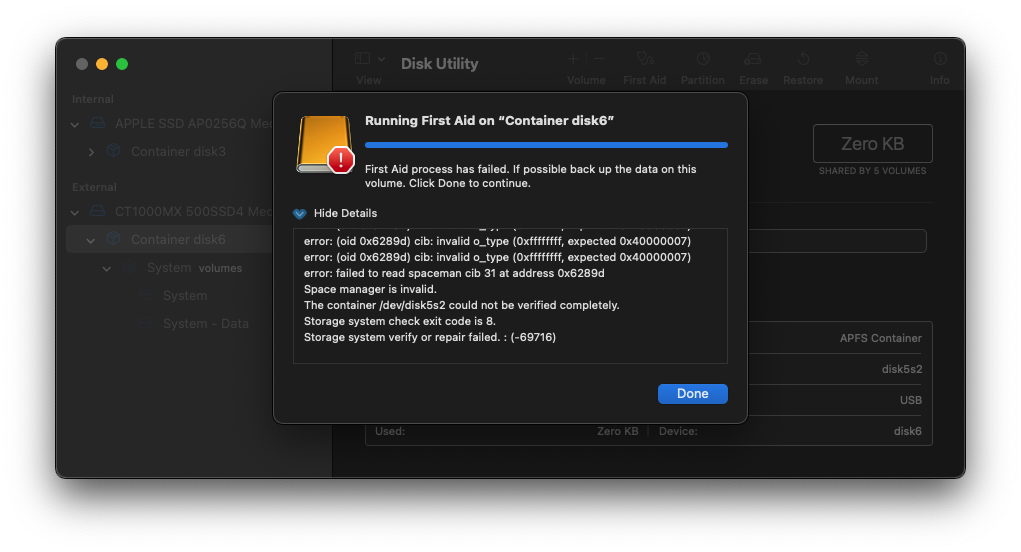
It'll also show 'Space manager is invalid.' If you try to run First Aid on the 'System - Data' volume, you'll get error -69845:
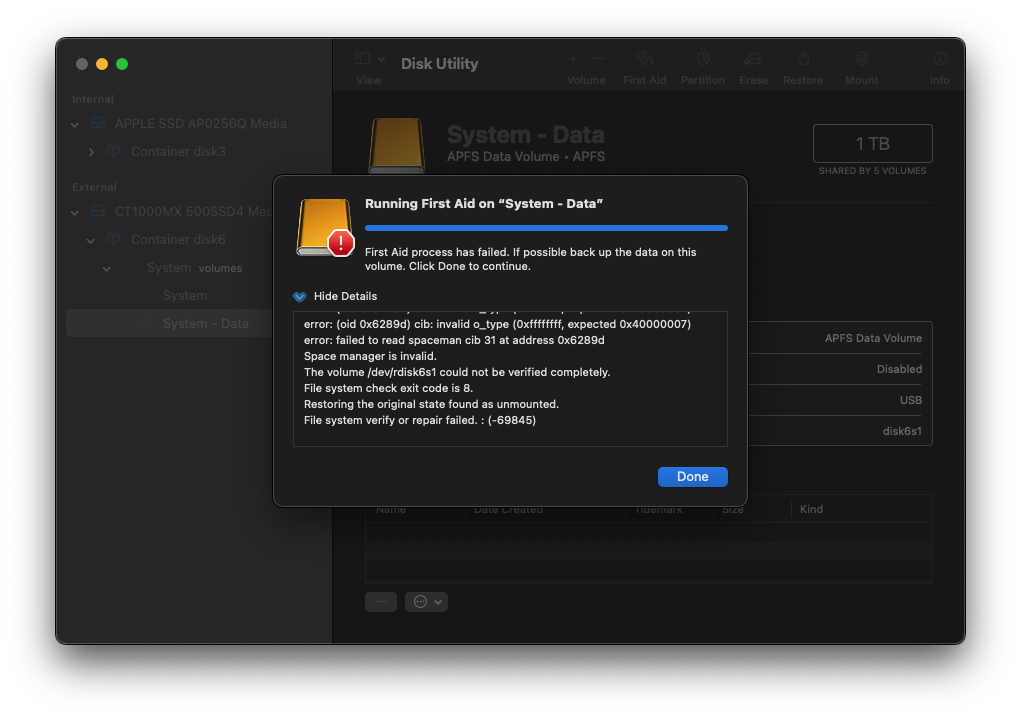
But let's back up here (ha). The System - Data volume is usually the first volume in the container, and it's where your user data is. The other System volume is for the actual operating system, macOS.
By running First Aid on the container, you get the drive identifier — for me, here, it's
We'll need python3, which can be installed through homebrew in Terminal. If you don't have homebrew, get it here:

Then for python3 it's as simple as
You'll also need DRAT:

 github.com
github.com
I downloaded the pre-compiled binary

 github.com
github.com
However, once downloaded, macOS won't allow you to run it:
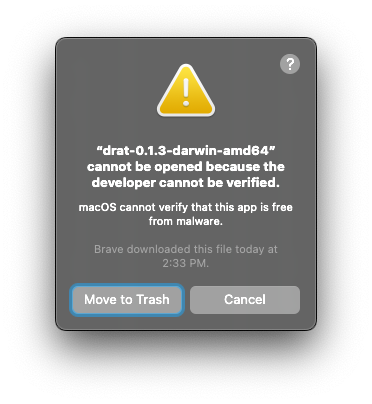
You'll need to remove that flag in terminal with
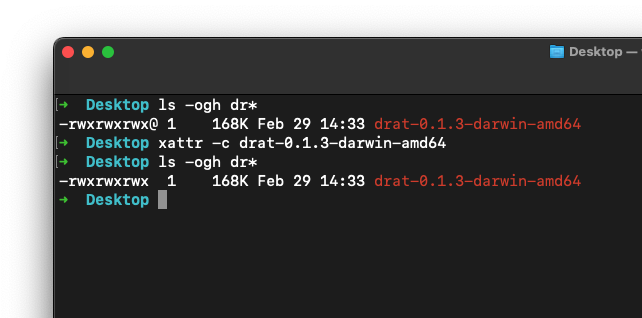
Once installed you can play around with it by typing
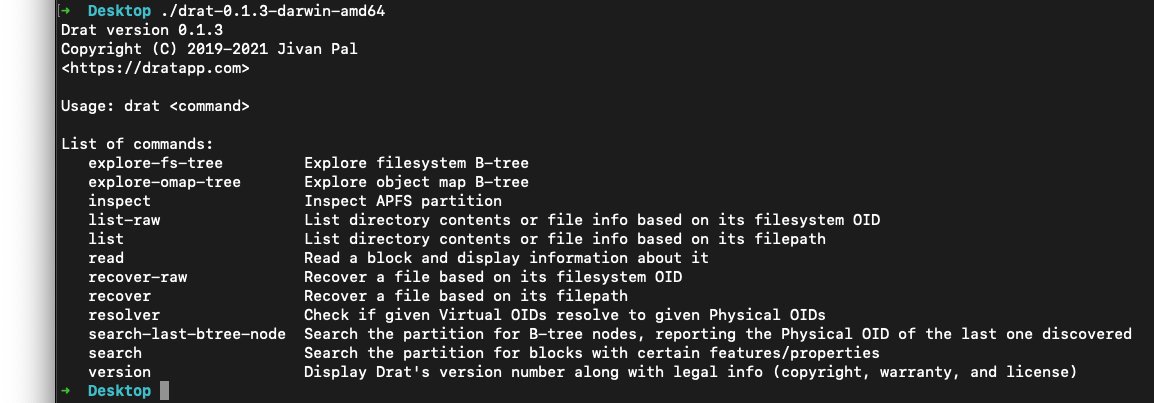
We'll use
That's listing out my container,
That folder structure needs to be recreated on where you want the data saved, this is because I don't know python and we're using someone else's script to recover this directory.
That script is

 github.com
github.com
Here's the modified code to work with
A summary of the modifications:
That's it, you're on your way to recovering your data. Once it's done and verified, you can wipe the crashed drive and put it back to use.
Addendum, this is what
As of today, there aren't any publicly available tools or utilities that can fix filesystem errors that may happen with either internal or external drives that lose power unexpectedly.
But you can recover data from the drive using another computer/device.
There are three ways:
1. Use an iOS device with a Type-C connector, and connect the drive through a USB adapter. This can read the files directly through the Files app, allowing you to copy data right off the seemingly crashed drive. You'll need a device with enough internal storage to recover the files that you need.
2. Use a paid app, there are a few. They usually offer a free download to browse through the drive after you've connected it to another Apple computer with a USB adapter, these are about $90 for a one-month subscription but quickly give you a 50% discount if you decline to pay after the entire drive has been indexed.
3. This guide.
But first, the symptoms. You'll need to enable 'Show All Devices' in Disk Utility's View menu:
This allows you to see the APFS containers:
And when you attempt to run First Aid on the container, you get an exit code 8 with error -69716:
It'll also show 'Space manager is invalid.' If you try to run First Aid on the 'System - Data' volume, you'll get error -69845:
But let's back up here (ha). The System - Data volume is usually the first volume in the container, and it's where your user data is. The other System volume is for the actual operating system, macOS.
By running First Aid on the container, you get the drive identifier — for me, here, it's
/dev/disk5s2. That's where I'll be performing the recovery.We'll need python3, which can be installed through homebrew in Terminal. If you don't have homebrew, get it here:

Then for python3 it's as simple as
brew install python in Terminal.You'll also need DRAT:
GitHub - jivanpal/drat: Utility for performing data recovery and analysis of APFS partitions/containers.
Utility for performing data recovery and analysis of APFS partitions/containers. - jivanpal/drat
I downloaded the pre-compiled binary
drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64 straight to the Desktop, you'll find it on the releases page:Releases · jivanpal/drat
Utility for performing data recovery and analysis of APFS partitions/containers. - jivanpal/drat
However, once downloaded, macOS won't allow you to run it:

You'll need to remove that flag in terminal with
xattr -c drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64:Once installed you can play around with it by typing
./drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64 in Terminal to see what options are available, we'll be using list and recover.We'll use
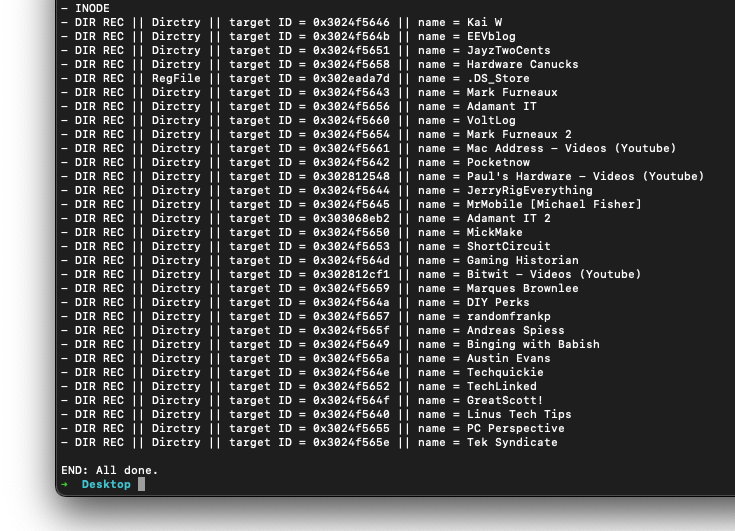
list first to recreate the folder structure, here I'm trying to recover my gPodder downloads of a few Youtube channels by typing out:sudo ./drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64 list /dev/disk5s2 0 /Users/samosa/gPodder/DownloadsThat's listing out my container,
disk5s2, volume 0 which is first volume in the container, System - Data, and the path to the folder where my files are. This is what I see at the end of a wall of text:That folder structure needs to be recreated on where you want the data saved, this is because I don't know python and we're using someone else's script to recover this directory.
That script is
recover.py from memecode on github:apfs-tools/recover.py at master · memecode/apfs-tools
Open-source toolset for analysing APFS partitions/containers. - memecode/apfs-tools
Here's the modified code to work with
drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64 instead of apfs-list and apfs-recover:
Python:
import os
import sys
import subprocess
import io
import time
from pathlib import Path
dev = "/dev/disk5s2"
idx = "0"
folder = "/Users/samosa/gPodder/Downloads"
out = "/Volumes/Vault/Macbook/gPodder/Downloads"
exclude = []
paths = []
# stats
last_ts = 0.0
list_errors = 0
list_count = 0
list_total = 125267
# list_total = 8891
recover_errors = 0
def ls(path):
global list_errors, list_count
dirs = []
files = []
args = ["./drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64", "list", dev, idx, path]
p = subprocess.run(args, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
list_count = list_count + 1
if p.returncode == 0:
lines = p.stderr.decode("utf-8")
for ln in lines.split("\n"):
if ln.find("- DIR REC") >= 0:
parts = ln.split("||")
if len(parts) >= 4:
name = parts[-1].strip().split("=")[-1].strip()
if parts[1].strip() == "Dirctry":
dirs.append(name)
else:
files.append(name)
else:
list_errors = list_errors+1
print("\n" + " ".join(args))
return [dirs, files]
def scan(path):
global total, last_ts, paths, list_errors, list_count
for e in exclude:
if e == path:
return 0
dirs,files = ls(path)
for f in files:
paths.append(path + "/" + f)
if time.time() - last_ts > 2.0:
print("Scanning", len(paths), "files...", "%.1f%%" % (len(paths)*100.0/list_total), "(%i errors %.1f%%)" % (list_errors, list_errors*100.0/list_count))
last_ts = time.time()
# and then scan the subfolders...
for d in dirs:
s = path + "/" + d
scan(s)
scan(folder)
if 1:
start_ts = time.time()
created = dict()
for progress, i in enumerate(paths):
fld,leaf = os.path.split(i)
part = fld[len(folder):]
# check if we need to create output folder?
outdir = out + leaf
if outdir not in created and not os.path.isdir(outdir):
# os.makedirs(outdir)
created[outdir] = True
if not leaf == ".DS_Store":
o = out + part + "/" + leaf
# print(i, "->", o)
# if not os.path.exists(o) or Path(o).stat().st_size == 0:
if 1:
args = ["./drat-0.1.3-darwin-amd64", "recover", dev, idx, i]
outfile = open(o, "wb")
p = subprocess.run(args, stdout=outfile, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
if not p.returncode == 0:
recover_errors = recover_errors + 1
print(" ".join(args))
outfile.close()
if time.time() - last_ts > 2.0:
last_ts = time.time()
elapsed = last_ts - start_ts
if elapsed > 0.0:
rate = progress / elapsed
if rate > 0:
remaining_files = len(paths) - progress
remaining_time = remaining_files / rate
hrs = int(remaining_time / 3600)
remaining_mins = remaining_time - (hrs * 3600)
min = int(remaining_mins / 60)
sec = int(remaining_mins) % 60
# print(remaining_files, remaining_time, rate, hrs, min, sec)
print("Exporting", progress, "of", len(paths), "(%.2f%%)" % (progress * 100.0 / len(paths)), "files...", "("+str(recover_errors), "errors)", "%ih%im%is @ %.1f" % (hrs, min, sec, rate))A summary of the modifications:
- Line 8 has the identifier for the container we want to recover from.
- Line 9 has the volume number.
- Line 10 is the source path.
- Line 11 is the destination path with the folder structure recreated inside.
- Line 12 has excludes emptied out.
- Line 27/28 has apfs-list replaced with drat list.
- Line 78/79 is commented out because I don't know python and this script glitches when making folders.
- Line 86/87 has apfs-recover replaced with drat recover.
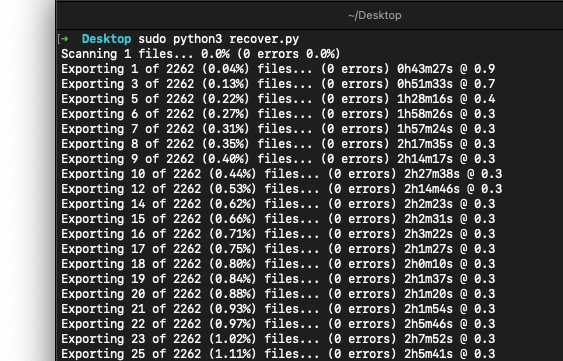
chmod 777 recover.py in Terminal then you can run it with sudo python3 recover.py:That's it, you're on your way to recovering your data. Once it's done and verified, you can wipe the crashed drive and put it back to use.
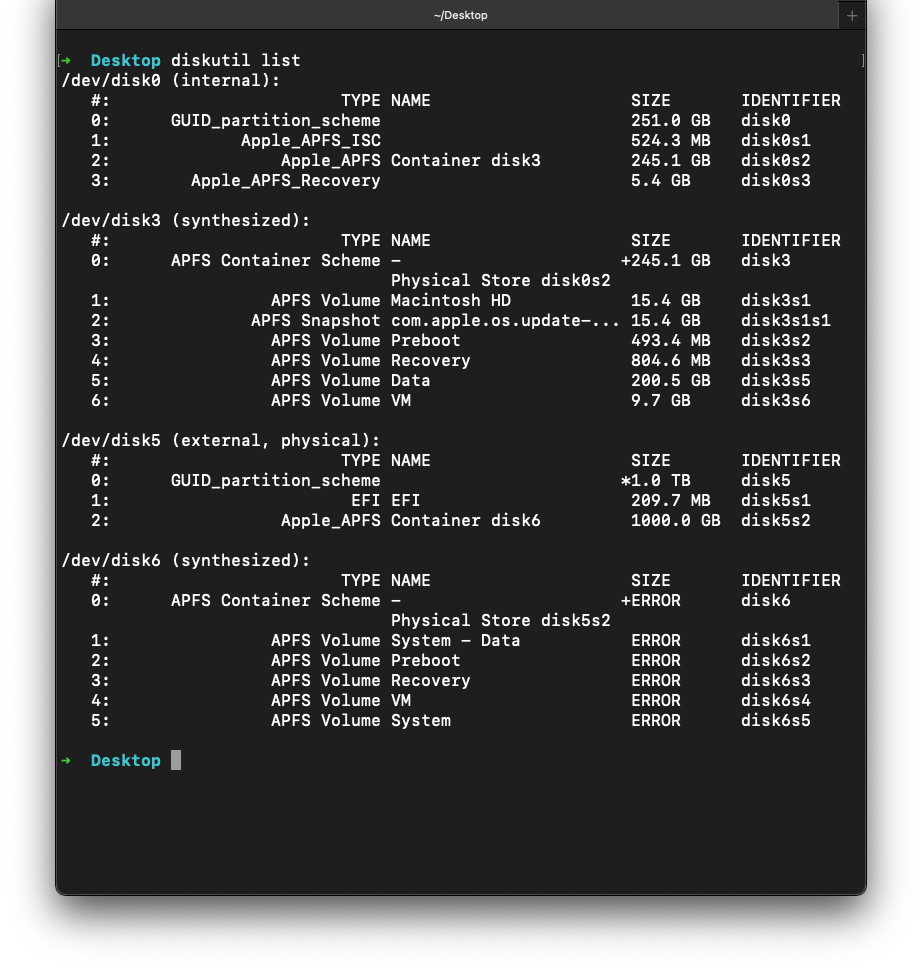
Addendum, this is what
diskutil list shows with a crashed drive:
Last edited: