IPS abridged for In-Plane Switching is a newer variety of LCD panels. The older generation TN panels had limitations of colour reproduction and viewing angles. IPS solves these issues albeit compromising response times a little. IPS panels give excellent colour reproduction which is unrivalled in the LCD's and it also provides maximum viewing angles better than any of its counterparts. It has revolutionized photo editing and video editing. Newer IPS have taken the monitor arena by storm.
IPS though is still an enigma among many. Its aspects are confusing to many. In this article I strive to explain it in detail.
Workings of an IPS
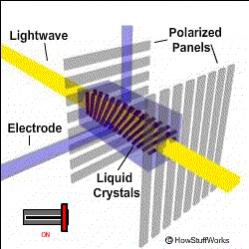
The LCD works as a filter layer filtering which rays of light reach us. The TN panels do this by modulating the angles between the molecules of the crystal layers. this is amply elucidated by the below image.
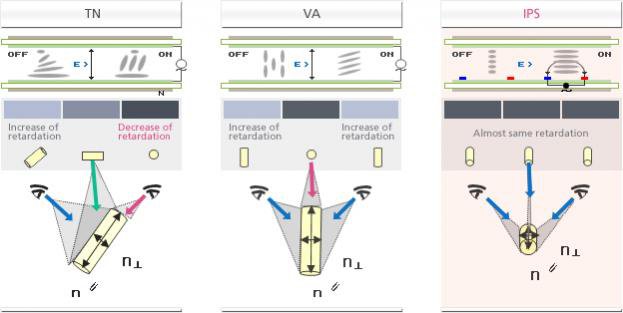
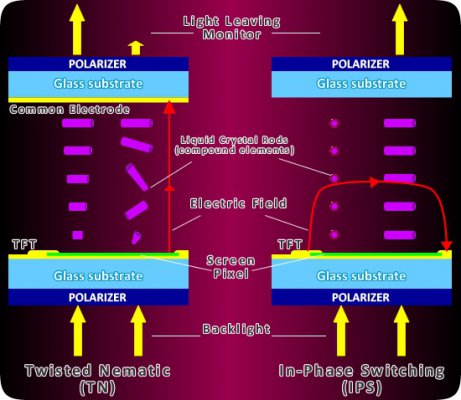
The IPS however uses a different approach. Instead of the gradual untwisting noticed above, the molecules of the liquid layer in the IPS panels completely rotate 90 degrees to allow light to pass through. So this results in all the molecules of the liquid crystal layer being in a single direction, all in a plane parallel to the screen. In this sense it is like a light switch either totally on or totally off. This results in the image being viewed from any angle without a problem unlike a TN panel wherein at certain angles only partial rays can be seen. This is illustrated by the image below.
This has it disadvantages though. To modulate such a layer two transistors are required instead of one utilized in a TN panel. This causes more power requirements as well as decreased area of transparency resulting in use of more powerful backlights which causes the backlight bleed issues of several IPS panels.
Types of IPS panels
The IPS panels can be subdivided majorly as
1. S-IPS
2. H-IPS
1. S-IPS: The S-IPS or the Super-IPS is the original prototype of the IPS panels.The older versions were plagued by very slow response times, sometimes as long as 60ms!! Several new improvements have been made to the S-IPS which have vastly improved its response time mainly using the response time compensation(RTC) technology. It still lacks the level of contrast of VA panels. Various improvements of the S-IPS include
i. E-IPS: The 'Enhanced IPS' is a type of S-IPS with faster response times compared to the older gen. Also the viewing angles were further improved upon in E-IPS along with contrast ratios. Here is a link for further reference
http://www.tftcentral.co.uk/download...nced_s-ips.pdf
ii. AS-IPS: Advanced Super-IPS is another itineration of S-IPS which is similar in all aspects to the E-IPS..
2. H-IPS: The Horizontal IPS was developed by rearranging pixels in a S-IPS to have more density of pixels for a better viewing experience and a reduced backlight bleed. Its varieties include
i. e-IPS: The 'economy-IPS' not to be confused with E-IPS that stands for enhanced IPS. Its is a cost effective and simpler version of the H-IPS. It is part of majority of the IPS panels used in desktop computing today. Viewing angles are slightly lesser than traditional H-IPS or S-IPS but very easy to produce.
ii. p-IPS: Performance IPS. They have true 8bit and an extended gamut, also good contrast. slightly better than the e-IPS
iii. P-IPS: Professional IPS. Best of the IPS panels. have true 10bit colur. Best colour reproduction and best contrast. most expensive among the consumer IPS panels.
Newer varieties are being researched everyday and are basically mprovements of these.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
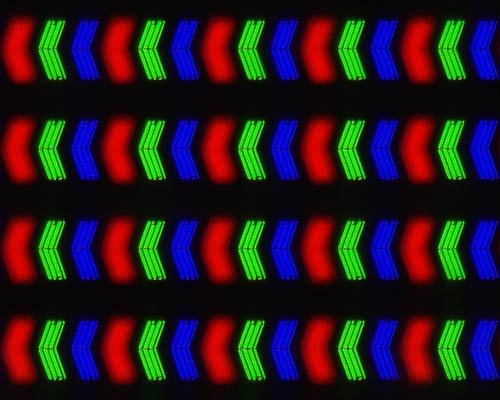
1. Exceptional colour reproduction. Unlike a TN in an IPS the whole colour is displayed with no spreading of charge to adjacent pixels. This allows a particular colour to be displayed avidly. In a TN adjacent pixels may be excited causing overlap of colours sometimes as seen below.
2. Large viewing angles. upto 180 degrees.. The reason for this has been explained in the workings section. An example is given below
Disadvantages
1. Contrast is lesser than some panels. This is because greater amount of the transparent area is utilized for the transistors than other panels
2. Response times are slower than TN panels. This may cause image lag or motion blur sometimes.. Nowadays this has been improved by Response Time compensation mechanisms inbuilt in the IPS developed by LG
IPS though is still an enigma among many. Its aspects are confusing to many. In this article I strive to explain it in detail.
Workings of an IPS
The LCD works as a filter layer filtering which rays of light reach us. The TN panels do this by modulating the angles between the molecules of the crystal layers. this is amply elucidated by the below image.
[attachment=9568:16327.attach]
The IPS however uses a different approach. Instead of the gradual untwisting noticed above, the molecules of the liquid layer in the IPS panels completely rotate 90 degrees to allow light to pass through. So this results in all the molecules of the liquid crystal layer being in a single direction, all in a plane parallel to the screen. In this sense it is like a light switch either totally on or totally off. This results in the image being viewed from any angle without a problem unlike a TN panel wherein at certain angles only partial rays can be seen. This is illustrated by the image below.
[attachment=9569:16328.attach]
This has it disadvantages though. To modulate such a layer two transistors are required instead of one utilized in a TN panel. This causes more power requirements as well as decreased area of transparency resulting in use of more powerful backlights which causes the backlight bleed issues of several IPS panels.
Types of IPS panels
The IPS panels can be subdivided majorly as
1. S-IPS
2. H-IPS
1. S-IPS: The S-IPS or the Super-IPS is the original prototype of the IPS panels.The older versions were plagued by very slow response times, sometimes as long as 60ms!! Several new improvements have been made to the S-IPS which have vastly improved its response time mainly using the response time compensation(RTC) technology. It still lacks the level of contrast of VA panels. Various improvements of the S-IPS include
i. E-IPS: The 'Enhanced IPS' is a type of S-IPS with faster response times compared to the older gen. Also the viewing angles were further improved upon in E-IPS along with contrast ratios. Here is a link for further reference
http://www.tftcentral.co.uk/download...nced_s-ips.pdf
ii. AS-IPS: Advanced Super-IPS is another itineration of S-IPS which is similar in all aspects to the E-IPS..
2. H-IPS: The Horizontal IPS was developed by rearranging pixels in a S-IPS to have more density of pixels for a better viewing experience and a reduced backlight bleed. Its varieties include
[attachment=9570:16329.attach]
S-IPS pixel structure
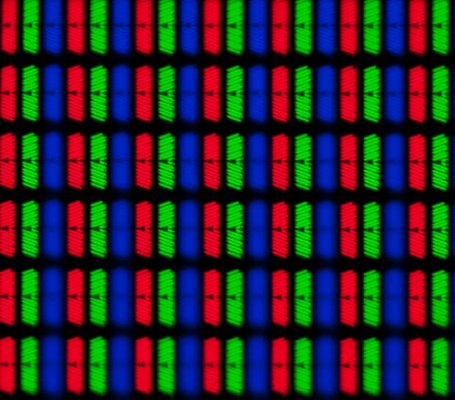
[attachment=9571:16330.attach]
H-IPS pixel structure
S-IPS pixel structure
[attachment=9571:16330.attach]
H-IPS pixel structure
i. e-IPS: The 'economy-IPS' not to be confused with E-IPS that stands for enhanced IPS. Its is a cost effective and simpler version of the H-IPS. It is part of majority of the IPS panels used in desktop computing today. Viewing angles are slightly lesser than traditional H-IPS or S-IPS but very easy to produce.
ii. p-IPS: Performance IPS. They have true 8bit and an extended gamut, also good contrast. slightly better than the e-IPS
iii. P-IPS: Professional IPS. Best of the IPS panels. have true 10bit colur. Best colour reproduction and best contrast. most expensive among the consumer IPS panels.
Newer varieties are being researched everyday and are basically mprovements of these.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
1. Exceptional colour reproduction. Unlike a TN in an IPS the whole colour is displayed with no spreading of charge to adjacent pixels. This allows a particular colour to be displayed avidly. In a TN adjacent pixels may be excited causing overlap of colours sometimes as seen below.
[attachment=9574:16333.attach]
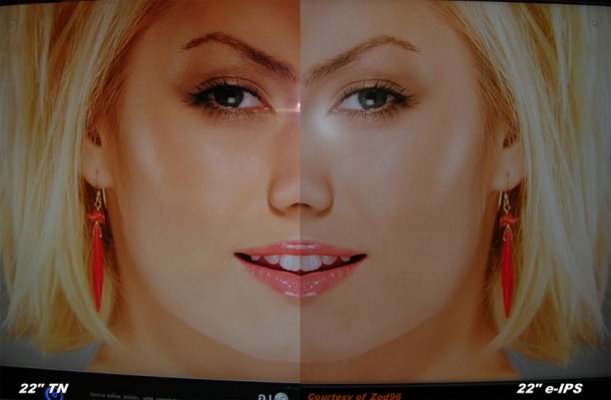
2. Large viewing angles. upto 180 degrees.. The reason for this has been explained in the workings section. An example is given below
[attachment=9572:16331.attach]
Disadvantages
1. Contrast is lesser than some panels. This is because greater amount of the transparent area is utilized for the transistors than other panels
[attachment=9573:16332.attach]
2. Response times are slower than TN panels. This may cause image lag or motion blur sometimes.. Nowadays this has been improved by Response Time compensation mechanisms inbuilt in the IPS developed by LG
[attachment=9580:16339.attach]
[attachment=9581:16340.attach]
[attachment=9581:16340.attach]
Attachments
-
 lcd.jpg13.6 KB · Views: 113
lcd.jpg13.6 KB · Views: 113 -
 ips_layout.jpg26.5 KB · Views: 131
ips_layout.jpg26.5 KB · Views: 131 -
 s-ips_structure.jpg58.6 KB · Views: 111
s-ips_structure.jpg58.6 KB · Views: 111 -
 h-ips_structure.jpg81.6 KB · Views: 107
h-ips_structure.jpg81.6 KB · Views: 107 -
 s-ips_colorshift-eagle_500x500.jpg39.3 KB · Views: 120
s-ips_colorshift-eagle_500x500.jpg39.3 KB · Views: 120 -
 tnvseips01.jpg40.8 KB · Views: 114
tnvseips01.jpg40.8 KB · Views: 114 -
 43InPlaneSwitching-IPS.jpg81 KB · Views: 108
43InPlaneSwitching-IPS.jpg81 KB · Views: 108 -
 dell_u2311h.jpg51.7 KB · Views: 104
dell_u2311h.jpg51.7 KB · Views: 104 -
 samsung_2233rz_120.jpg30.2 KB · Views: 115
samsung_2233rz_120.jpg30.2 KB · Views: 115